About Me

Hello, I'm Vedant Shah
I'm a Machine Learning Researcher passionate about Artificial Intelligenece (AI). Presently, I'm pursuing my Ph.D in Computer Science at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign , having completed my Master's in computer science at Virginia Tech . My academic journey has been marked by a strong GPA of 4.0, reflecting my dedication and commitment to my field.
My research interests lie at the intersection of parameter-efficient fine-tuning, multimodal learning, deep generative models, and data quality. My work is dedicated to developing robust methodologies that improve fine-tuning efficiency and uncertainty estimation in calibration of generative AI models. My master's thesis, Are Particle-Based Methods the Future of Sampling in Joint Energy Models? A Deep Dive into SVGD and SGLD explored different classical sampling techniques to improve calibration of image classification models. In parallel, I'm also leveraging foundation models (FMs) for uncertainty elicitation in open-world settings, aiming to improve AI robustness and interpretability.
My technical prowess spans across Deep Learning, and Data Science, with proficiency in frameworks and libraries like PyTorch, Mediapipe, Transformers (Hugging Face), NTLK, ONNX, OpenCV, and Scikit-Learn. Additionally, I have extensive experience in data engineering and visualization using Pandas, NumPy, Seaborn, and Matplotlib.
I have had the privilege of working under, Dr. Ismini Lourentzou, in the Perception and Language Lab , both at Virginia Tech and now at UIUC. My previous experiences also include a research internship at the Laboratory for Fluid Dynamics in Nature , where I led the development of a machine learning model for blood pressure variation detection by leveraging photoplethysmography signals and regression analysis for understanding hemodynamics.
I have also served as a reviewer for AAAI, PETRA, ICCV, and ICML conferences, contributing to the broader research community. You can learn more through my publications and research projects.
Beyond research, I have served as a teaching assistant for five semesters across diverse courses, ranging from core programming to capstone projects, fostering both technical and collaborative skills in my students. Outside of academia, I enjoy swimming, working out, hiking, and playing badminton. I am driven by the values of commitment, curiosity, excellence, and integrity, striving to embody them in all my pursuits.
Research
Publication:

[Data] Quality Lies In The Eyes Of The Beholder
Xavier Plemming, Vedant Shah, Ismini Lourentzou
Keywords: Datasets, Data Quality, Data Utility, User Survey, Data Analytics.
ACM PETRA 2022 Association for Computing Machinery Pervasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments
Abstract: As large-scale machine learning models become more prevalent
in assistive and pervasive technologies, the research community
has started examining limitations and challenges that arise from
training data, e.g., fairness, bias, and interpretability issues. To
this end, data-centric approaches are increasingly prevailing over
time, showing that high-quality data is a critical component in
many applications. Several studies explore methods to define and
improve data quality, however, no uniform definition exists. In
this work, we present an empirical analysis of the multifaceted
problem of evaluating data quality. Our work aims at identifying
data quality challenges that are most commonly observed by data
users and practitioners. Inspired by the need for generally applicable
methods, we select a representative set of quality indicators, that
covers a broad spectrum of issues, and investigate the utility of these
indicators on a broad range of datasets through inter-annotator
agreement analysis. Our work provides insights and presents open
challenges in designing improved data life cycles.
Paper
DOI

Uncertainty in Action: Confidence Elicitation in Embodied Agents
Vedant Shah
Keywords: Embodied AI, Agents, Uncertainty Elicitation, Open-World Understanding.
ArXiv 2025
Abstract: Expressing confidence is challenging for embodied agents navigating dynamic multimodal environments, where uncertainty arises from both perception and decision-making processes. We present the first work investigating embodied confidence elicitation in open-ended multimodal environments. We introduce Elicitation Policies,
which structure confidence assessment across inductive, deductive, and abductive reasoning, along with Execution Policies, which enhance confidence calibration through scenario reinterpretation, action sampling, and hypothetical reasoning. Evaluating agents in calibration and failure prediction tasks within the Minecraft environment, we show that structured reasoning approaches, such as Chain-of-Thoughts, improve
confidence calibration. However, our findings also reveal persistent challenges in distinguishing uncertainty, particularly under abductive settings, underscoring the need for more sophisticated embodied confidence elicitation methods.
Paper
DOI

Are Particle-Based Methods the Future of Sampling in Joint Energy Models? A Deep Dive into SVGD and SGLD
Vedant Shah
Keywords: Variational Inference, Stein Variational Gradient Descent, Joint Energy Models, Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods, Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics.
VTechWorks 2024
Abstract: This thesis explores advanced techniques for improving machine learning models with a focus on developing well-calibrated and robust classifiers. We concentrated on two methods, Stein Variational Gradient Descent (SVGD) and Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics (SGLD), to evaluate their effectiveness in enhancing classification accuracy and reliability. Our research introduced a new mathematical approach to improve the stability and performance of Joint Energy Models (JEMs). By leveraging the generative capabilities of SVGD, the model is guided to learn better data representations, which are crucial for robust classification. Using the CIFAR-10 image dataset, we confirmed prior research indicating that SGLD, particularly when combined with an optimization method called Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM), delivered the best results in terms of accuracy and stability. Notably, SVGD without SAM, despite yielding slightly lower classification accuracy, exhibited significantly lower calibration error, making it particularly valuable for safety-critical applications. However, SVGD required careful tuning of hyperparameters and substantial computational resources. This study lays the groundwork for future efforts to enhance the efficiency and reliability of these advanced sampling techniques, with the overarching goal of improving classifier calibration and robustness with JEMs.
Paper
DOI
Poster Presentation:
 Vedant Shah, Julia WakeField, Anne Staples
Vedant Shah, Julia WakeField, Anne Staples
Virginia Tech Summer Research Symposium 2022
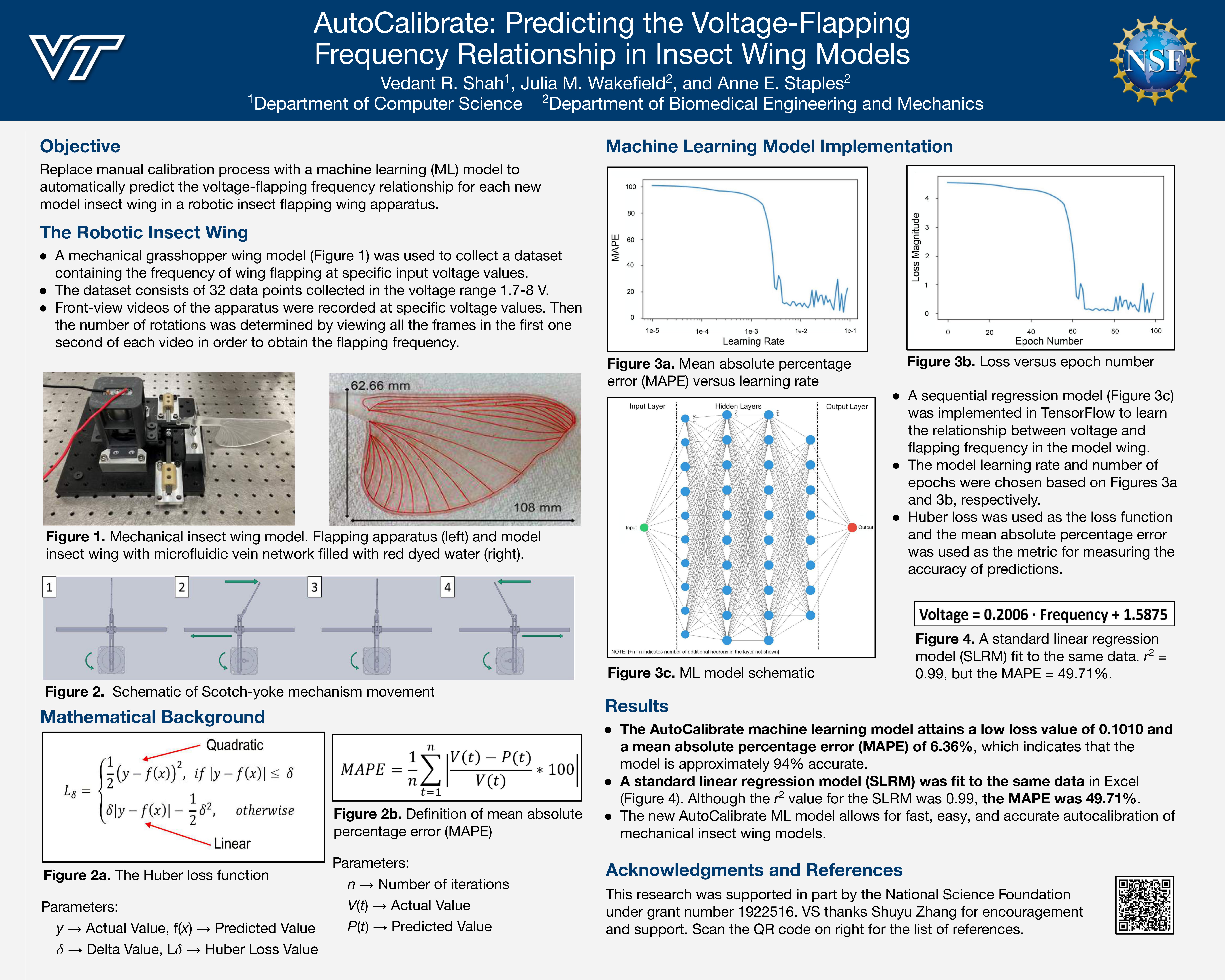
Abstract: A mechanical insect wing station has been constructed to understand the underlying fluid dynamic principles which guide the circulation of hemolymph in an insect wing.
The frequency at which the wing flaps depends on the voltage fed to the motor and on the inertial properties of the wing. Using machine learning (ML) to perform regression,
estimating the values of dependent variables based on independent variables, is a well-studied task both in academia and industry. While many generic regression models are available,
we wanted to be able to calibrate the apparatus for new wings using only sparse data. A custom regression model was built using Tensorflow with the adaptive moment estimation algorithm
(Adam) as the optimization function and Huber as the loss function to learn the relationship between the voltage and frequency of specific insect wing models fabricated with stereolithography
resin printers. Datasets were prepared by manually tracking the flapping wing in video data in order to find the flapping frequency in Hertz and the voltage from the power source in Volts at
that frequency. The mean absolute percentage error is used to measure the accuracy of the prediction. The model predicts voltage based on input frequency with a 94% success rate. Automating
this manual task with an ML model improves the accuracy of values. This is essential to improve data accuracy in the insect wing hemodynamics experiments which has a broader application to
downstream tasks such as developing systems for drug delivery and other applications in human health.
High-Res Poster Pdf
Abstract [pg 203]
Code
 Adaliah Duyna, Cayla Catz, Jessica Prisbe, Vedant Shah, Shuyu Zhang, Anne Staples
Adaliah Duyna, Cayla Catz, Jessica Prisbe, Vedant Shah, Shuyu Zhang, Anne Staples
Virginia Tech Summer Research Symposium 2022
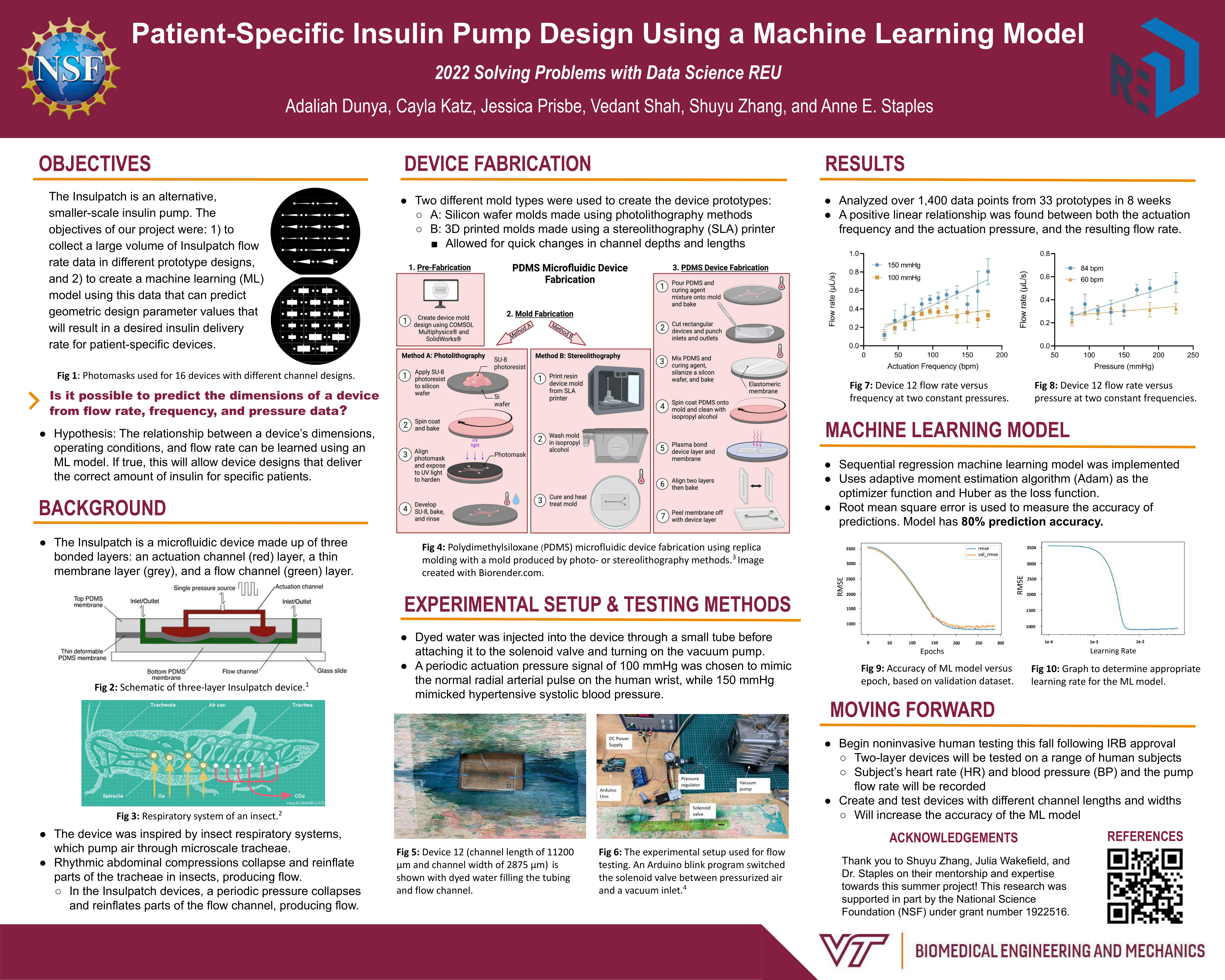
Abstract: Over 500 million people are affected by diabetes worldwide. For insulin-dependent patients, treatments include bulky and inconvenient battery-powered insulin pumps and painful syringe injections.
The InsulPatch is an alternative, smaller-scale insulin delivery pump currently under development. It provides an inexpensive way to administer insulin easily, painlessly, and without a power source,
making insulin delivery more convenient for Type 1 diabetics. Inspired by the insect respiratory system, the InsulPatch features a multilayer microfluidic pump system. It uses the wearer’s radial pulse to
pump insulin transdermally via a microneedle array. Photolithography and stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing microfabrication techniques were used to create device design molds. The molds were then used
to create the InsulPatch device layers by pouring liquid polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) into the molds and baking to cure the PDMS. The devices contain three layers: a top layer consisting of actuation channels,
a thin middle membrane, and a bottom layer containing the flow channels. Flow rate data was collected at different actuation pressures and frequencies for different flow and actuation channel geometric design
parameters. The devices were actuated using pressurized air signals representing different blood pressures and heart rates. The flow rate data was collected and analyzed using Graphpad Prism. This data was then
used to create a sequential regression machine learning model with 80% prediction accuracy, enabling the solution of the inverse problem of producing device designs for specific patients. After successful clinical
trials, the InsulPatch will allow for accessible, painless, and convenient insulin delivery.
High-Res Poster Pdf
Abstract [pg 123]
Code
 John Do, Vedant Shah , Yoon Choi, Anne Staples
John Do, Vedant Shah , Yoon Choi, Anne Staples
Institute for Creativity, Arts, And Technology Day 2023
Abstract: 1 in 4 women experience intimate partner violence. Safety Tank, is a simple tank top with a detachable device created to detect unusual linear and rotational accelerations associated with interpersonal violence.
By utilizing an accelerometer and gyroscope, the device can accurately monitor changes in motion, including forceful falls. When a concerning event occurs, Safety Tank generates alerts that are immediately sent to predetermined contacts,
such as healthcare providers, intervention teams, and trusted friends.
High-Res Poster Pdf
Demo Video
Contact